Release: AWS Management Portal for vCenter
Amazon Web Services (AWS) released at May 30 2014 the ‘AWS Management Portal for vCenter‘. This free plug-in for vCenter allows management of virtual machines and virtual networks running on Amazon Web Service from the vSphere Client.
AWS Management Portal also allows to import a vSphere virtual machine to AWS. The VMware virtual machine needs to be shutdown to perform a conversion to the Amazon .AMI format (used by the Xen based hypervisor) as well as the upload to an Amazon datacenter.
The Management Portal plug-in also offers self-service access to AWS.
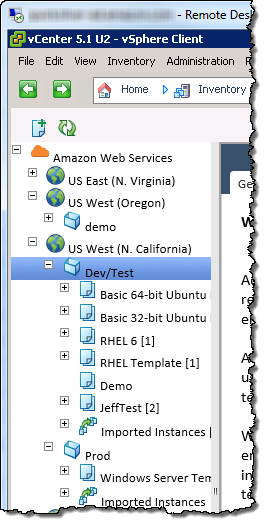
A single console now provides management of both VMware on-premises infrastructures as well as Amazon public clouds. This is not a comprehensive tool for creating and managing AWS resources. The management portal enables vCenter users to get started quickly with basic tasks, such as creating a VPC and subnet, and launching an EC2 instance. To complete more advanced tasks, users must use the AWS Management Console or AWS CLI.
A comprehensive step by step description of the features of AWS Management Portal is published on amazon.com.
AWS Management Portal is distributed as a .OVA file which can easily imported into vCenter Server. Download here.
VMware is not happy with this plug-in. Mind there has been a conversion tool for VMware>Amazon available for a while. In a blogpost Chris Wolf, CTO for America warns customers for the Hotel California effect. VM’s in Amazon are hard to export back to on-premises. More importantly, an import of a VM is the easy task. Customers however want a uniform way of management, API’s and ability to use the same set of tools and procedures for both on-premises as well as for public cloud. Amazon offers totally different features than vSphere.
VMware offers its VMware owned and operated public cloud named vCloud Hybrid Service which has the same features as vSphere on-premises. For example it offers vMotion capabilities which Amazon does not have.